Why Adults Learn Languages Faster Than Children (A Data-Driven Post)

I like to collect all sorts of nonsensical sayings about language learning. There is an overabundance of them, but one of my favorites is: "children learn quickly."
"Nonsense?!" you might say with indignation. "Don't all children speak well at a young age?"
No.
I don't think we should be putting on a pedestal the mental achievements of a being for whom one of the more impressive skills is the ability to fart and sneeze simultaneously.
But let's not rely on guesses and assumptions. It's time to put on some "scientific" trunks and dive into the sea of scientific research to find out what the real pace of children's learning is
Why Adults Learn Languages Faster
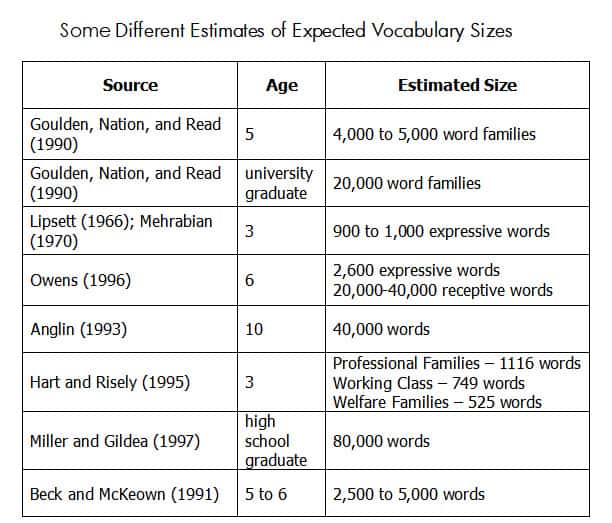
SIZE OF VOCABULARY IN CHILDREN AGED 1-7 years
To be able to count anything, we need to start with basic data and look at the average vocabulary of children aged 12 months (when they start to say the first words) up to the age of 7.
Due to the availability of data on this subject, I will use the numbers given for an average American child. I think that these numbers will still be a decent reflection of the average child for other languages, especially considering that English is one of the most lexically developed languages in the world.
DEFINITION OF WORDS
Remember that in linguistics, there is no single and strict definition of a word. Depending on the data, one word is, well, just one word (a unique selection and order of letters). In other studies, the word and all its inflections are counted as one word. For example, according to this classification, the words "jump," "jumped," "jumping," etc. are treated as one word. If you see a particularly large number in this table, it means that each word is counted separately.
The other data pool describes the average expressive vocabulary of children as follows:
SIZE OF VOCABULARY IN CHILDREN - EXCEPTIONS
Of course, it is worth remembering that this is average data. Depending on the child's intellectual predisposition and the upbringing, he or she may develop faster or slower.
For example, a child in the ninetieth percentile at 16 months knows the same number of words as a 26-month-old child in the tenth percentile.
Why this range?
There is at least one study (Hart and Risley, 2006), which suggests that the size of the vocabulary of a child aged three is closely related to the number of conversations that adults have with this child. Interestingly, the differences in language development and IQ in such children were still visible at the age of nine!
It is, of course, only a curiosity for anyone interested, especially current and future parents.
Let's return to our example. We already have the most important data; now, it is time for some calculations to prove that adults learn languages faster than children.
How Many Words a Day Does an Average Child Learn?

As an example, let's choose a 5-year-old child. And not just any child! Suppose he is little John von Neumann, and he already knows 6,000 words - a number that is well above the average for this age.
Of course, let us assume that the child of this age also has decent grammar and can put these words together quite appropriately.
This extraordinarily well-developed child had about 1,825 days from birth, or 1,460 days since pronouncing the first word, to master 6,000 words.
His average learning pace is therefore:
- 3.29 words per day (from birth)
- 4.11 words per day (from 12 months)
How do these numbers make you feel?
I can only assume that "Well, four words a day. Respect. Hats off. How do they do it?!" is not the first thought to cross your mind. There is nothing impressive about these numbers. Instead, they show one thing: young children learn very slowly.
If you can stand the deadly pace of learning 5 words per day, you'll do better than our wise, exemplary child. It's heartwarming, eh?
The Pace of Learning in Older Children
It is worth remembering that for every person, also for a child, the so-called snowball effect applies.
The snowball effect states that the greater your knowledge (especially in a given field), the faster you can learn.
It means, more or less, that the older the child is, the more new words will be learned per day on average. Many sources say that later in adolescence, this number ranges between 10-14 words (Lipsett / Mehrabian and Owens numbers are from Language Development - An Introduction; Robert E. Owens, Jr .; Allyn and Bacon; 1996).
I will repeat my question: Is such a pace in any way crazy and exceeds the capabilities of an adult? Surely not.
Remember that the snowball effect also applies to you - the more words you know, the faster you will learn more. Besides, as an adult, you have a whole range of attributes and skills unavailable to children:
All these factors make you a real harvester of knowledge!
Adults Learn Languages Faster - Summary
Let it be said again - adults learn languages faster than children!
I have witnessed incredible language acquisitions of people who thought that they could not learn quickly (or that it was impossible), and who within 10 months reached the level of B1 / B2 in the language of their choice (you can read more about it here).
Such a pace of learning exceeds the abilities of even the most gifted children. I think that if we would like to learn something from children, it would be to be persistent in pursuing a goal.
I hope that moving forward you will be more optimistic about your abilities!
Done reading? Time to learn!
Reading articles online is a great way to expand your knowledge. However, the sad thing is that after barely 1 day, we tend to forget most of the things we have read.
I am on the mission to change it. I have created over 13 flashcards that you can download to truly learn information from this article. It’s enough to download ANKI, and you’re good to go. This way, you will be able to speed up your learning in a more impactful way.