Interleaved Practice – When and How to Use It to Maximize Your Learning Pace

We've all heard that practice makes perfect. It takes time and effort to be great at something, and if you want to do it right, you should practice one skill at a time.
For example, a beginning guitarist might rehearse scales before chords. A young tennis player practices the forehand before the backhand.
This phenomenon is called “blocking,” and because it appeals to common sense and is easy to schedule, blocking is dominant in schools, training programs, and other settings.
However, the question we should be asking ourselves is this: is blocking the most optimal way to practice skills? It doesn't seem so.
What is interleaving?
Interestingly, there is a much better strategy - enter "interleaving".
In interleaving one mixes, or interleaves, practice on several related skills together. In other words, instead of going AAAAABBBBBCCCCC you do ABCABCABCABC.
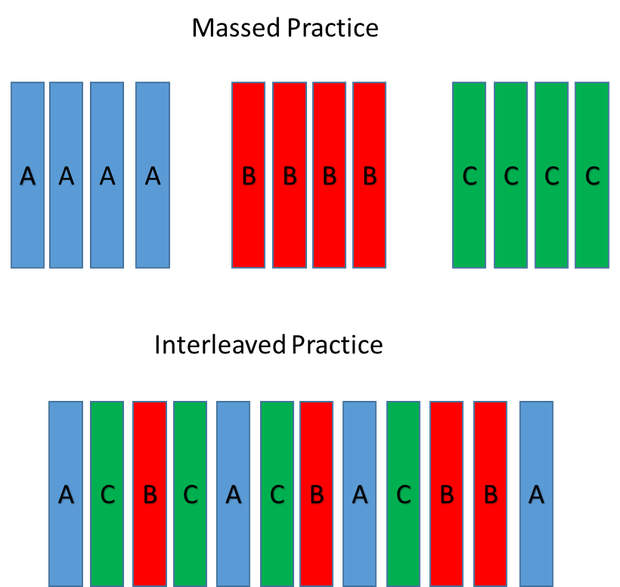
It turns out that varying it even slightly can yield massive gains in a short period.
Let's take baseball as an example: Batters who do batting practice with a mix of fastballs, change-ups, and curveballs hit for a higher average. The interleaving is more effective because when you're out there in the wild, you need first to discern what kind of problem you're facing before you can start to find a solution, like a ball coming from a pitcher's hand.
Read more: A Simple Learning Plan To Get The Most Out Of Your Study Time.
Is interleaved practice always the right choice?
There are almost no strategies that are fully universal and can be used for all disciplines and in all learning conditions. The same goes for interleaved practice.
The past four decades definitely demonstrated that interleaving often outperforms blocking for a variety of subjects, but especially motor learning (e.g., sports). The results for other subjects are mixed.
Studies on interleaved practice in different disciplines
1. Languages
For example, when native English speakers used the strategy to learn an entirely unfamiliar language (i.e., generating English-to-Swahili translations), the results were better, the same, or worse than after blocking.
2. Mathematics
Another study (Rohrer et al., 2015) concerning mathematics showed the dramatic benefits of interleaving on children’s performance at math.
During the experiment, some kids were taught math the traditional way. They got familiar with one mathematical technique in a lesson and then practiced it to death. A second group was given assignments that included questions necessitating the use of different techniques.
The results were as impressive as they were surprising.
One day after the test, the students who’d been utilizing the interleaving method did 25% better. However, when tested a month later, the interleaving method did 76% better.
Keep in mind that such an increase is truly amazing, given that both groups had been learning for the same amount of time. The only difference was that some students learned block by block, and others had their learning mixed up.
Read more: How To Master Many Fields Of Knowledge - Your Action Plan And Recommended Strategies.
The necessary condition before you apply interleaved practice



The results above tell us one important thing. You can't just go cowabunga and start interleaving the heck out of every subject.
Before you do so, you should have some familiarity with subject materials (or the materials should be quickly or easily understood). Otherwise, as appears to be the case for foreign languages, interleaving can sometimes be more confusing than helpful.
It's only logical when you look at this strategy from the memory perspective. For many, using even one technique seems to a burden enough for their working memory. Forcing such people to use three or more make you a psycho who wants to see the world, and their memory, burn.
It's simply too much.
It doesn't take away from the fact that interleaving can be extremely useful. It forces the mind to work harder and to keep searching and reaching for solutions.
However, if you decide to use it, make sure that you're familiar with the strategies you want to interleave. This recommendation is based on a phenomenon called the expertise reversal.
The expertise reversal
The expertise reversal effect occurs when the instruction that is effective for novice learners is ineffective or even counterproductive for more expert learners.
If you look at it differently, more experienced learners learned more from high variability rather than low variability tasks demonstrating the variability effect. In contrast, less experienced learners learned more from low rather than top variability tasks showing a reverse variability effect.
Why might lower variability be better in the beginning?
It was suggested that more experienced learners had sufficient available working memory capacity to process high variability information. In contrast, less experienced learners were overwhelmed by high variability and learned more using low variability information. Subjective ratings of difficulty supported the assumptions based on cognitive load theory, which you have learned before.
In other words, some signals that are needed by low prior knowledge learners might be redundant for high prior knowledge learners due to their existing schema in long-term memory (Kalyuga, 2009).
For example, one of the experiments (Likourezos, Kalyuga, Sweller, 2019) which tested 103 adults studying pre-university mathematics, showed no interaction between levels of variability (high vs. low) and levels of instructional guidance (worked examples vs. unguided problem solving). The significant main effect of variability indicated a variability effect regardless of levels of instructional guidance.
What does it tell us?
We can't play in the big boy's league if we don't cover the basics!
Read more: The Curse of the Hamster Wheel of Knowledge – Why Becoming a Real Expert Is Very Difficult.
Interleaved Practice - Summary
(1) Interleaved practice is perfect for:
- motor learning
- any material that can be quickly learned and understood
(2) For more complicated subjects, make sure to familiarize yourself with the appropriate strategies before you decide to interleave them. This way, you will make sure that your working memory isn't overburdened.
Done reading? Time to learn!
Reading articles online is a great way to expand your knowledge. However, the sad thing is that after barely 1 day, we tend to forget most of the things we have read.
I am on the mission to change it. I have created over 11 flashcards that you can download to truly learn information from this article. It’s enough to download ANKI, and you’re good to go. This way, you will be able to speed up your learning in a more impactful way.











Definitely! When I try to explain this to my teammates or people I coach, I call this the “law of diminishing returns”.
Let’s say your goal is to practice 500 free throws each day. However, if you do them all without taking a break, your first 10 will teach you far more than attempts 240-250. If you take breaks – and let your default mode network consolidate the information while you focus on other tasks – then you can maintain a high degree of learning for all 500 repetitions.
Personally, I do find that attempts 240-250 (in the above metaphorical situation) require way more discipline than attempts 1-10 to remain focused and engaged, but it’s still vastly better than practicing with a block schedule! I try to switch up my task every 10-15 minutes, though I plan these switches beforehand to minimize context-switching costs ^^
This is such a great example! You’re absolutely right. Once the habituation kicks in, you stop paying attention to any details, and to the action itself in the end 🙂
This article brings a bridge across two ideas I had: First, Interleaving practice is better for learning. Second, why do I (and other people as well) often find it more confusing than anything? Even when trying hard.
I share the point of view that, high working memory is critical to be able to learn complex topics deeply. I think that may be why students often take notes of subjects carefully until they have a more digestible version of their informations.
Great points, Ene! Although I wouldn’t say that better working memory is critical for learning complex skills. It can easily be substituted by your background knowledge and/or mnemonics 🙂